Recent court decisions in Canada on HIV non-disclosure are bad science, bad public health policy, and bad medicine for women, says Louise Binder The theme of the 57th session of the UN Commission on the Status of Women now underway in New York is gender-based violence.
UK: New research calls for better guidance for HIV service providers on criminal law, confidentiality and ethics
Yesterday saw the release of an important new UK study, Keeping Confidence: HIV and the criminal law from service provider perspectives, which explores how HIV criminalisation impacts those who deliver health and social care services for people with HIV.
The report’s lead author, Dr Catherine Dodds, from Sigma Research at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said: “Although HIV health and social care professionals expressed diverse views about their potential role in such cases, they gave a clear sense that criminal prosecutions for the transmission of HIV would not improve public health. Instead, it was most common to hear descriptions of such cases leading to increased stigma, reduced trust between service users and providers, and traumatic consequences for those involved in such cases.”
Study co-investigator, Matthew Weait, Professor of Law and Policy at Birkbeck, Univerisity of London, said: “This important and innovative research demonstrates both the problems that HIV criminalisation creates for clinical and social care providers and the need for solutions at both national and regional level. Care providers working in HIV and sexual health are concerned primarily with the health and wellbeing of their service users – which is of course as it should be; but there is also evidence that criminalisation is compromising their work. Increased awareness and understanding of, and inter-organisational communication about, legal issues is critical, and Keeping Confidence makes practical recommendations as to how that work might be taken forward for the benefit of prevention and support.”
Roger Pebody from aidsmap.com does an excellent job of summarising the study and its findings in this news report:
The study explored how criminal prosecutions for HIV transmission in England and Wales are handled by those who deliver clinical, psychosocial and community support for people with HIV. The report paints a picture of professionals grappling with the difficulties of communicating complex legal information in an appropriate way for each individual. They must weigh up competing concerns and responsibilities, including their own patient’s health and wellbeing, the health of unidentified sexual partners and the legal liability of their own organisation.
The report was launched in central London yesterday at a one-day meeting attended by around 70 HIV service providers, representatives of most of the UK’s community-based HIV organisations, and people living with HIV.
Following presentations of the report’s main findings, a panel consisting of a health adviser, and representatives of community-based organisaton and a people living with HIV discussed the implications for them.
Ceri Evans, Senior Health Adviser at the West London Centre for Sexual Health, Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, highlighted that there may not be a ‘best time’ to inform a newly diagnosed individual of their new legal obligations. Athough she agreed that the post-testing counselling session may not be ideal, she noted that since the criminal law potentially covers all sexually transmissable infections, including genital herpes, and there is usually only a single oppportunity to provide counselling following a new herpes diagnosis, that information about the law might need to be provided to some patients sooner rather than later.
Of note, the report’s fieldwork, involving 75 providers of HIV health and social care services in England and Wales, was undertaken in the latter half of 2012. Since then, the British HIV Association (BHIVA) and the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) have released an updated position statement on HIV Transmission, the Law and the Work of the Clinical Team which provides clinicians with information and guidance on managing many of the issues highglighted as problematic in the research. Lead author, Dr Mary Poulton, Consultant and Clinical Lad, Sexual Health and HIV, Kings College Hospital, London, outlined the main recommendations and provided case studies that illustrated how the decision-guiding algorithm regarding third-party disclosure might be particularly useful.
The rest of the meeting focused around discussing the report’s recommendations, which were as follows.
National recommendations
1. HIV service professionals will benefit from a single website or webpage that collates practical and accessible information about criminal prosecutions for the sexual transmission of HIV. It will need to be updated as new resources become available, and older ones are revised. New resources should be published as required in order to keep pace with clinical and scientific developments in the treatment of HIV that may impact on legal decision-making. The online resource can also identify the best sources of expert criminal legal advice where those are available.
2. A nation-wide programme of continuous professional development in the criminal law should be available to those who provide clinical and non-clinical HIV services. Topics covered should include: straightforward legal definitions and defence arguments, how and when to raise discussions about legal responsibilities, professional liability, communication skills development through the use of scenarios, and existing policy and practice models.
3. Key contacts with an interest in criminal prosecutions should be identified in each clinical and non-clinical HIV service organisation.This process should feed into the development of an updated list for the explicit use of disseminating information about information and training discussed in recommendations 1 and 2 above.The key contacts will also be utilised as the main organisational contact for the development and dissemination of resources to inform people with HIV about the law in this area.
Local recommendations
4. Existing professional guidance and associated documents should be discussed and adapted for local use. This will translate differently in specific settings, and it may lead to the development of local criminalisation policies or protocols, or values statements in some workplaces. At a minimum, such activities should strive for internal consistency on advice, facilitation and support.
5. Opportunities should be created for clinics and community-based organisations to exchange best practice as it relates to criminal prosecution for HIV transmission and to discuss where they agree and disagree on a conceptual level about the ethics of responsibility and public health in HIV prevention.
6. Alongside the development of local criminalisation protocols, all organisations will need to review their confidentiality policies, ensuring that they are accessible to service users, and compatible with internal agreements about criminalisation.
Whilst there was broad consenus regarding many of the recommendations, implementation will depend on various stakeholders collaborating, as well as sufficient funding.
Of note, currently only Australia has a website on HIV and the law aimed specifically at HIV healthcare professionals. The Australian Association of HIV Medicine (ASHM) online Guide to Australian HIV Laws and Policies for Healthcare Professionals covers civil, criminal and public health law, and also includes reference to national guidance on the Management of People with HIV who Place Others at Risk.
The entire day was filmed by the HIV Justice Network and video of the main presentations and final disussion outcomes will be available soon.
US: Fake NBC news website claimed NY police wanted man for intentional HIV transmission
Friday, a news report from an NBC affiliate in New York circulated the web via blogs claiming that police were searching for a man named Isaac Don Burks for intentionally spreading HIV in the NY Tri-State area. On Monday, the original source was called into question when the link being shared redirected to an Augusta news site.
The original source came from a fake site made to look like the NBC New York 4 website. The slight difference was in the domain. The real NBC affiliate’s domain is www.nbcnewyork.com the fake site used www.nbcnewyork4.com. The original story url still shows up in Google search as http://nbcnewyork4.com/news/local/fugitive-wanted-for-intentionally-spre… yet you no longer go to the original report. Instead, when you click on the link you are directed to an Augusta story about the same man, but for a different incident in 2010 involving identity fraud and forgery.
US: Journalist Todd Heywood discovers that Michigan health department have been secretly collecting HIV testing information for the past decade
Since 2003, the Michigan Department of Community Health has been secretly collecting the names, dates of birth, risk categories, and other demographic information of people submitting for confidential HIV testing at grant-funded locations throughout the state and storing them in a massive database, a months-long investigation by The American Independent has discovered.
US: New study to explore effects of HIV criminalisation on health department policies and programmes
The Medical College of Wisconsin’s (MCW) Center for AIDS Intervention Research (CAIR) has received a one year, $50,000 grant to study the tensions the criminalization of HIV exposure creates in public health, and the resulting impact on clients. Carol Galletly, J.D., Ph.D., associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral medicine at CAIR, is the primary investigator. Zita Lazzarini, J.D., M.P.H., director of the division of public health law and bioethics at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine, is co-principal investigator.
The goals of the study are to identify where and how the criminalization of HIV exposure has influenced health department policies and programs, and to examine how staff members in public health departments resolve the tensions between criminal law, public health authority, and patient-centered care when considering the prospect of an HIV-positive client knowingly exposing others to HIV. “Criminal law and public health law have markedly different philosophies and approaches to HIV prevention. Those often mutually exclusive approaches result in people not being tested, and individuals who are HIV-positive unknowingly transmitting the virus. This study will examine some of the basic questions about the impact of the law on public health,” said Dr. Galletly.
New UK report finds HIV criminalisation impact on healthcare workers
Sigma Research undertakes social research to inform policy and practice concerning HIV and sexual health.
Greek HIV case – Interview with Zoe Mavroudi from Radiobubble
We’re working to support Radiobubble to produce a documentary about the Greek HIV case – the women who were arrested and imprisoned after forced HIV tests. Zoe Mavroudi is directing the documentary. Here Radiobubble interviews her about the progress of the case and the making of the documentary.
OnMedica – News – HIV positive patients fail to disclose their infection to NHS staff
A significant proportion of HIV positive patients may not be disclosing their infection to NHS staff, when turning up for treatment at sexual health clinics. This is the finding suggested by preliminary research published online in the journal Sexually Transmitted Infections .
US: President’s AIDS council calls on feds to help states repeal HIV criminalisation laws
Advisory group says these statutes are ‘unjust’ and fuel the epidemic
BY TODD HEYWOOD, AMERICAN INDEPENDENT
The Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS (PACHA) passed a resolution last week that calls for an end to federal and state HIV-specific criminal laws and prosecutions.
While the resolution is only advisory, it recommends that the departments of Justice and Health and Human Services issue guidance and offer incentives to state attorneys general and state health departments to eliminate HIV-specific laws. The advisory group also asks these federal agencies to develop guidelines for how to approach HIV within criminal and civil justice systems that are “consistent with the treatment of similar health and safety risks.”
As the resolution notes, 32 states and two territories have laws criminalizing people living with HIV.
In explaining the reason to repeal these laws, the resolution reads:
People living with HIV have been charged under aggravated assault, attempted murder, and even bioterrorism statutes, and they face more severe penalties because law enforcement, prosecutors, courts, and legislators continue to view and characterize people living with HIV and their bodily fluids as inherently dangerous, even as ‘deadly weapons. Punishments imposed for non-disclosure of HIV status, exposure, or HIV transmission are grossly out of proportion to the actual harm inflicted and reinforce the fear and stigma associated with HIV. Public health leaders and global policy makers agree that HIV criminalization is unjust, bad public health policy and is fueling the epidemic rather than reducing it.
PACHA is also requesting that state and federal authorities review the cases of persons convicted under such laws and overturn convictions if deemed appropriate. The group is calling on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to “issue a clear statement addressing the growing evidence that HIV criminalization and punishments are counterproductive and undermine current HIV testing and prevention priorities.”
“Today’s announcement is an important advancement in our collective effort to modernize unjust and discriminatory HIV criminalization laws,” said Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.), co-chair of the Congressional HIV/AIDS Caucus in a statement last week. Lee introduced the REPEAL HIV Discrimination Act in 2011, which never passed, and served on the United Nations’ Global Commission on HIV and the Law.
“I join the President’s Advisory Council on AIDS in calling on the Department of Justice and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention to issue clear guidance to states and public health departments on the counterproductive effects of HIV criminalization policies; we must end this clear discrimination against people living with HIV,” Lee continued. “Criminalization laws breed fear, discrimination, distrust and hatred, and we must end them.”
The White House declined to comment on the resolution, but the National HIV/AIDS Strategy adopted by the Obama administration in July 2010 does call for state legislatures to “consider reviewing HIV-specific criminal statutes to ensure that they are consistent with current knowledge of HIV transmission and support public health approaches to preventing and treating HIV.”
Policymakers at the state level also welcomed the resolution. Randy Mayer, chief of the Bureau of HIV, STD, and Hepatitis for the Iowa Department of Public Health, said the resolution was a new tool in advocates’ fight to repeal Iowa’s HIV-specific law.
“This resolution came at an excellent time for Iowa,” Mayer said in an email to The American Independent.
State activists and public health officials, including Mayer, have laid out a strategy to repeal the state’s law.
“The advocates in Iowa have also aligned their efforts with a public health perspective, so the resolution was a reinforcement of their justification,” Mayer said. “I think the more public health entities that weigh in on this discussion the better.”
But while policymakers praise the resolution, activists urge cautious optimism.
Sean Strub, executive director of the anti-HIV-criminalization organization Sero Project, said the resolution was appreciated, but the “real test will be in whether federal agencies and the administration responds with the necessary urgency.”
Catherine Hanssens, executive director of the Center for HIV Law and Policy, which runs the Positive Justice Project, echoed Strub’s sentiment, noting that while the resolution is important, PACHA “has no power to order anyone to do anything.”
“[HHS] Secretary [Kathleen] Sebelius and President Obama both have the discretion to ignore the resolution’s recommendations.”
Regardless, Hanssens said the resolution is an important milestone in the battle to repeal HIV criminal laws in the U.S.
“The work of advocates who pushed for passage of the resolution is not over,” she said. “But we have passed a major marker on the road to reform, and justice, for many people and communities affected by HIV.”
UK: Updated guidance on HIV transmission, the law and the work of the clinical team now published
The British HIV Association (BHIVA) and the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) have produced updated guidance on HIV Transmission, the Law and the Work of the Clinical Team.
This guidance is aimed at those working in the field of HIV medicine, especially clinicians, but will also be of use to general practitioners and people living with HIV who want to understand the legal and medical basis for some of their care decisions.
The guidance begins with a clear statement against HIV criminalisation:
BHIVA and BASHH believe that this use of the law is unhelpful and potentially harmful to public health and support UNAIDS recommendations to limit the use of criminal law and the Oslo declaration view that a “non-punitive, non-criminal HIV prevention approach” is preferable.
Covering the law in England & Wales as well as Scotland, the document aims to provide information and guidance on managing issues related to sexual transmission of HIV based on current scientific evidence. It applies generic ethical and professional principles but with a greater emphasis on providing a confidential environment in which extremely sensitive matters can be frankly and fully discussed. This enables appropriate care of people with HIV and benefits public health by encouraging individuals to access testing and treatment. Within this framework this document sets out the roles and responsibilities of health care professionals when caring for individuals living with HIV.
Consistent with the recent BHIVA and the Expert Advisory Group on AIDS (EAGA) position statement on the use of antiretroviral therapy to reduce HIV transmission, the guidance notes:
In most situations the appropriate use of antiretroviral treatment is at least as effective as condoms in preventing sexual transmission of HIV. This is accepted by the [Crown Prosecution Service of England and Wales] and [Scottish Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service] so it is likely that evidence showing that the defendant was taking effective antiretroviral treatment at the time of the alleged transmission may be used to demonstrate that they were not reckless.
The guidance also clearly states that healthcare professionals “must be mindful of their duty not to work beyond their expertise in legal matters. For people with HIV, advice must include the routes of HIV transmission and how to prevent transmission, with information about safer sexual practices, the use of condoms and suppression of viral load. Advice must be given in a non-judgmental way.”
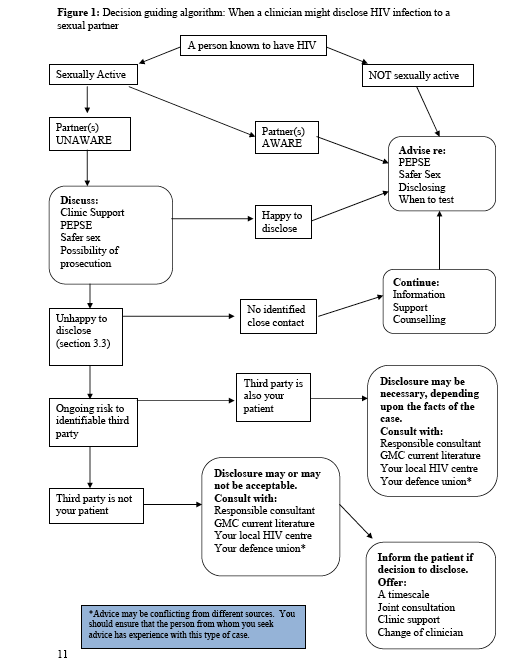
It also discusses issues of confidentiality, noting that “it is important when considering breaching confidentiality to weigh up all potential harms as there may be situations where disclosure of HIV status to protect a sexual partner results in considerable harm to an individual e.g. domestic violence. In situations where a health care professional believes that an HIV positive individual continues to put sexual contacts at risk their duties and subsequent action depend upon the type of contact.” See Figure 1 below.
The guidance also clearly states that “no information should be released to the police unless patient consent has been verified or there is a court order in place, except in very limited circumstances defined by the [General Medical Council].”
Importantly, it also notes that only individuals can make complainants to the police “and health care workers should remain impartial during discussions with patients.”
Finally, it provides clear advice to both help prevent transmission of HIV to sexual partners and to avoid prosecution for ‘reckless’ HIV transmission. Accordingly, people with HIV should do at least one of the following:
- Use a male or female condom fitted correctly along with water-based lubricant. Individuals doing this are unlikely to be seen as reckless for legal purposes. In the event of a condom split, it is advisable to disclose HIV status in order to support the partner’s decision whether or not to obtain post-exposure prophylaxis (PEPSE), which should be taken within 72 hours. The need for PEPSE will depend upon the type of sexual activity and the HIV viral load. An assessment of the risk should be undertaken by a clinician according to the BASHH PEPSE guidelines. Disclosure in these situations would suggest that the person with HIV was not reckless.
- Adhere to effective (suppressed viral load) antiretroviral medication. There is growing evidence of extremely low/minimal risk of transmission when plasma HIV is fully suppressed with the use of antiretroviral medication. In some situations an undetectable viral load can afford protection equivalent to or greater than that of condoms. A person with HIV is unlikely to be seen as reckless when relying on a suppressed viral load instead of condom use if they have been counselled accordingly by an HIV clinician or similar medical authority. It is recommended that this discussion is documented in the patient’s medical records.
In addition people with HIV should be advised that disclosure of HIV positive status to a partner before sex is important to support informed agreement around risk and safer sex behaviours. To avoid successful prosecution an individual who is not taking effective antiretroviral medication and does not use a condom must disclose their HIV status to sexual partners before sex takes place.
The entire guidance is reproduced below.