More than 30 US states have laws criminalizing HIV exposure, transmission or non-disclosure of an individual’s HIV status. IN THE LIFE looks at the stigma and misinformation embedded in laws meant to curb the spread of the disease and the human cost among those who are HIV positive. Includes footage from the New York launch of the Positive Justice Project.
US: Positive Justice Project publishes essential new advocacy resource
The Center for HIV Law and Policy has released the first comprehensive analysis of HIV-specific criminal laws and prosecutions in the United States. The publication, Ending and Defending Against HIV Criminalization: State and Federal Laws and Prosecutions, covers policies and cases in all fifty states, the military, federal prisons and U.S. territories.
Ending and Defending Against HIV Criminalization: State and Federal Laws and Prosecutions is intended as a resource for lawyers and community advocates on the laws, cases, and trends that define HIV criminalization in the United States. Thirty-four states and two U.S. territories have HIV-specific criminal statutes and thirty-six states have reported proceedings in which HIV-positive people have been arrested and/or prosecuted for consensual sex, biting, and spitting. At least eighty such prosecutions have occurred in the last two years alone.
People are being imprisoned for decades, and in many cases have to register as sex offenders, as a consequence of exaggerated fears about HIV. Most of these cases involve consensual sex or conduct such as spitting and biting that has only a remote possibility of HIV exposure. For example, a number of states have laws that make it a felony for someone who has had a positive HIV test to spit on or touch another person with blood or saliva. Some examples of recent prosecutions discussed in CHLP’s manual include:
• A man with HIV in Texas is serving thirty-five years for spitting at a police officer;
• A man with HIV in Iowa, who had an undetectable viral load, received a twenty-five year sentence after a one-time sexual encounter during which he used a condom; his sentence was suspended, but he had to register as a sex-offender and is not allowed unsupervised contact with his nieces, nephews and other young children;
• A woman with HIV in Georgia received an eight-year sentence for failing to disclose her HIV status, despite the trial testimony of two witnesses that her sexual partner was aware of her HIV positive status;
• A man with HIV in Michigan was charged under the state’s anti-terrorism statute with possession of a “biological weapon” after he allegedly bit his neighbor.
The catalog of state and federal laws and cases is the first volume of a multi-part manual that CHLP’s Positive Justice Project is developing for legal and community advocates. The goal of the Positive Justice Project is to bring an end to laws and policies that subject people with HIV to arrest and increased punishment on the basis of gross ignorance about the nature and transmission of HIV, without consideration of the actual risks of HIV exposure.
The manual’s completion was supported by grants for CHLP’s anti-criminalization work and Positive Justice Project from the MAC AIDS Fund and Broadway Cares/Equity Fights AIDS.
Download the manual here (2.3MB)
US: Majority of gay US men support criminal non-disclosure laws
The overwhelming majority (70%) of HIV-negative and untested men (69%) in the United States support prosecutions for not disclosing known HIV-positive status before sex that may risk HIV transmission, according to a new study by Keith J. Horvatha, Richard Weinmeyera and Simon Rosser at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. Even more disturbing is the fact 38% of HIV-positive men endorsed criminalisation.
The most worrying finding is that suppport of non-disclosure laws strongly suggested a reliance on disclosure as an HIV prevention method. As I have discussed in HIV and the criminal law, this is unreliable and problematic.
There’s a summary of the study’s findings at aidsmap.com and the full text article can be downloaded here.
Global: HIV and the criminal law book now available; hear me speak in Ottawa and Toronto
The next few weeks sees my involvement in a flurry of anti-criminalisation advocacy in the United States and Canada, coinciding with the publication of the book version of the new international resource I produced for NAM and an article in HIV Treatment Update summarising the current global situation.
HIV and the Criminal Law
 |
||
| Email: info@nam.org.uk to order a copy |
Preface by The Hon. Michael Kirby AC CMG and Edwin Cameron, Justice of the Constitutional Court of South Africa.
Introduction How this resource addresses the criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission.
Fundamentals An overview of the global HIV pandemic, and the role of human rights and the law in the international response to HIV.
Laws A history of the criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission, and a brief explanation of the kinds of laws used to do this.
Harm Considers the actual and perceived impact of HIV on wellbeing, how these inform legislation and the legal construction of HIV-related harm.
Responsibility Looks at two areas of responsiblity for HIV prevention: responsibility for HIV-related sexual risk-taking and responsibility to disclose a known HIV-positive status to a sexual partner.
Risk An examination of prosecuted behaviours, using scientific evidence to determine actual risk, and how this evidence has been applied in jurisdictions worldwide.
Proof Foreseeability, intent, causality and consent are key elements in establishing criminal culpability. The challenges and practice in proving these in HIV exposure and transmission cases.
Impact An assessment of the impact of criminalisation and HIV – on individuals, communities, countries and the course of the global HIV epidemic.
Details: international resource and individual country data A summary of laws, prosecutions and responses to criminalisation of HIV exposure or transmission internationally, and key sources of more information.
HIV Treatment Update
The August/September issue of NAM’s newsletter, HIV Treatment Update, features a 2500 word article, ‘Where HIV is a Crime, Not Just a Virus’, that examines the current state of criminalisation internationally.
Here’s the first part: click on the image to download the complete article.
Since 1987, when prosecutions in Germany, Sweden and the United States were first recorded, an increasing number of countries around the world have applied existing criminal statutes or created HIV-specific criminal laws to prosecute people living with HIV who have, or are believed to have, put others at risk of acquiring HIV.
Most of the prosecutions have been for consensual sexual acts, with a minority for behaviour such as biting and spitting.
In the majority of these cases, HIV transmission did not occur; rather, someone was exposed to the risk of acquiring HIV without expressly being informed by the person living with HIV that there was a risk of HIV exposure.
In the cases where someone did test positive for HIV, proof that the defendant intended to harm them and/or was the source of the infection has often been less than satisfactory.
South Africa’s openly HIV-positive Constitutional Court Justice, Edwin Cameron, called for a global campaign against criminalisation at the 17th International AIDS Conference in Mexico City in 2008, declaring: “HIV is a virus, not a crime.”
Two years later, the discussion for people working in the HIV sector has moved on from a debate about whether such laws and prosecutions are good or bad public policy to one on how to turn the tide and mitigate the harm of criminalisation. Most of them advocate, in the long term, for decriminalisation of all acts other than clearly intentional HIV transmission. This, however, is a debate that many people outside the HIV sector have yet to even start.
Next Tuesday, September 21st, I’ll be joining a group of US anti-criminalisation advocates for a meeting in New York to discuss how to move towards mitigating the harm of US disclosure laws and prosecutions for HIV exposure and non-intentional transmission.
The goals of the Positive Justice Project campaign include:
- Broader public understanding of the stigmatizing impact and other negative public health consequences of criminalization and other forms of discrimination against people with HIV that occur under the guise of addressing HIV transmission.
- Community consensus on the appropriate use of criminal and civil law in the context of the HIV epidemic.
- Clear statements from lead government officials on the causes and relative risks of HIV transmission and the dangers of a criminal enforcement response to HIV exposure and the epidemic.
- A broader, more effective community-level response to the ongoing problem of HIV-related arrests and prosecutions.
- Reduction and eventual elimination of the inappropriate use of criminal and civil punishments against people with HIV.
Ottawa: September 29th 6pm-8pm
 |
| Click on the flyer to download |
I’ll be in Canada’s capital, Ottawa, on Wednesday September 29th to speak about my experiences of blogging on criminalisation worldwide, and to provide examples of international anti-criminalisation advocacy that Canadian advocates might find useful in their fight against the ramping up of charges for non-disclosure and the irrational and scare-mongering response to accusations of non-disclosure from law enforcement.
Ottawa has become ground zero for anti-criminalisation advocacy in recent months following the arrest and public naming and shaming of a gay man for non-disclosure. Following community outrage at the man’s treatment, the Ottawa Police Service Board rejected calls to develop guidelines for prosecution for HIV non-disclosure cases.
The meeting will also feature several leading lights in Canadian, if not global, anti-criminalisation advocacy: Richard Elliott, Executive Director of the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network; HIV-positive advocate David Hoe; and Eric Mykhalovskiy, Associate Professor at York University, Department of Sociology.
Toronto: September 30th 6.30pm-8.30pm
 |
| Click on image for link to Facebook event page |
The following day, Richard, Eric, myself and a fourth panellist (TBC) will be presenting at Silence, Sex and Science, Thursday, September 30, 2010, 6:30 to 8:30 pm at Oakham House, 55 Gould Street, Toronto.
I hope to meet any blog readers who can make it to either of the Canadian meetings, and will, of course, be posting more about these meetings in the future.
Canada: New report calls for prosecutorial guidelines to establish ‘significant risk’
A new report, launched at AIDS 2010 in Vienna last month, recommends that the Ontario Ministry of the Attorney General establish a consultation process to inform the development of prosecution guidelines for cases involving allegations of non-disclosure of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
HIV Non-Disclosure and the Criminal Law: Establishing Policy Options for Ontario contributes to the development of an evidence-informed approach to using the criminal law to address the risk of the sexual transmission of HIV infection in Ontario, and offers the most comprehensive, current discussion of the criminalisation of HIV non-disclosure in Canada.
The report was triggered by the absence of policy-based discussion of this issue amongst key decision makers in government and by community concerns about the intensified use and wide reach of the criminal law in circumstances of HIV non-disclosure.
In Canada, people living with HIV have a criminal law obligation to disclose their status before engaging in activities that pose a “significant risk” of HIV transmission. The report emphasises that uncertainties associated with that obligation and interpretations of the obligation that are not informed by current scientific research on HIV transmission risks are foundational to current problems in the use of the criminal law to regulate the risk of the sexual transmission of HIV and explores various forms of evidence relevant to a thorough policy consideration of the use of the criminal law in situations of HIV non-disclosure in sexual relationships.
York University has produced a 1200 word pdf summary of the report which I’m including in its entirety below. A pdf of the entire report can be downloaded here.
Title: The criminal law about sex and HIV disclosure is not clear
What is this research about?
According to the Supreme Court of Canada, HIV-positive people are required to disclose their status before engaging in sexual activities that pose a “significant risk” of transmitting HIV to a sex partner. Canadian courts, however, have yet to clearly define what sex acts, in what circumstances, carry a “significant risk.” This has led to an expansive use of the criminal law and created a problem for people with HIV—they can face criminal charges even though the law is not clear about when they must tell sex partners about their HIV. For example, people with HIV who are taking anti-HIV medications are much less likely to transmit HIV during sex, even where no condoms are used. But Ontario police and Crown Attorneys continue to interpret “significant risk” broadly. In fact, charges have been pursued in cases where, on a scientific level, there is little risk of HIV transmission.
This uncertainty has created problems not only for people with HIV but also for public health staff, and health care and social service providers. It has challenged these front-line workers in their attempts to counsel and support people with HIV. It has also caused many people with HIV to be further stigmatized. The media, in its coverage of these cases, has tended to exaggerate the risk of HIV transmission at a time when more and more experts have come to think of HIV as a chronic and manageable infection.
Despite these problems, and over 100 criminal cases in Canada, there has been a lack of evidence to inform public discussion about this important criminal justice policy issue. In Ontario, policy-makers have not weighed in publicly on the criminalization of people who do not reveal to their sex partners that they have HIV.
What did the researchers do?
A project team, led by Eric Mykhalovskiy, Associate Professor in the Department of Sociology at York University, set out to explore how the criminal law has been used in prosecutions involving allegations of HIV non-disclosure. The team included members of community organizations in Toronto and front-line workers, some of whom are living with HIV. Their goal was to create evidence and propose options to guide policy and law reform. They created the first national database on criminal cases of HIV non-disclosure in Canada. Professor Mykhalovskiy interviewed over 50 people with HIV, public health staff, and health care and social service providers to find out how the criminal law is affecting their lives or their work—another Canadian first.
What did the researchers find?
From 1989 to 2009, Canada saw 104 criminal cases in which 98 people were charged for not disclosing to sex partners that they have HIV. Ontario accounts for nearly half of these cases. Most of the cases have occurred since 2004. Half of the heterosexual men who have been charged in Ontario since 2004 are Black. Nearly 70% of all cases have resulted in prison terms. In 34% of these cases, HIV transmission did not occur.
Looking at the cases in Ontario and Canada, the researchers found inconsistencies in the evidence courts relied on to decide whether a sex act carried a significant risk of HIV transmission. They also found inconsistencies in how courts have interpreted the legal test established by the Supreme Court, and inconsistencies between court decisions in cases with similar facts. It appears, in some cases, that police and Crown prosecutors have not been guided by the scientific research when deciding whether to lay charges or proceed with a prosecution.
Because it is important to understand the scientific research when assessing whether there is a “significant risk” of HIV transmission during sex, the researchers included in their report a succinct summary of the leading science. The risk, in general, is low. Activities like unprotected sexual intercourse carry a risk that is much lower than commonly believed. Most unprotected intercourse involving an HIV-positive person does not result in the transmission of HIV. But the risk of transmission is not the same for all sex acts and circumstances. Antiretroviral therapy, however, can reduce the amount of HIV in a person’s bloodstream and make the person less infectious to their partner. Also, because of antiretroviral therapy, HIV infection has gone from being a terminal disease to a chronic, manageable condition in the eyes of many experts and people living with the virus.
Many people with HIV who were interviewed remain concerned that even if they disclose their HIV, their sex partners might complain to police. Health care and service providers stated that they are confused by the vagueness of the law. They also stated that criminalizing HIV non-disclosure prevents people from seeking the support they need to come to grips with living with HIV and disclosing to partners. But people with HIV and their providers have many suggestions for improving public policy and the law. The “significant risk” test needs to be clarified. The public health and criminal justice systems need to work together. And policies and procedures to guide Crown Attorneys need to be put in place.
How can you use this research?
Policymakers have several options to respond to the lack of clarity in the law and the resulting expansive use of the law. They can continue to let police, Crown Attorneys, and courts deal with cases as they arise. They can work to amend the Criminal Code. But the best solution, in the short term, would be the development of policy and procedures to guide Crown Attorneys working on these types of cases. The Ontario Ministry of the Attorney General should establish a consultation process to help develop policy and procedures for criminal cases in which people have allegedly not disclosed that they are HIV-positive to their sex partners.
What you need to know:
The criminal law can lead to very serious consequences for people who are charged or convicted. So policymakers need to make sure that the criminal law about HIV disclosure is clear and clearly informed by scientific research about HIV transmission. They also need to look to research to assess whether the law is having unintended consequences that get in the way of HIV prevention efforts.
About the Researchers:
Eric Mykhalovskiy is an Associate Professor and CIHR New Investigator in the Department of Sociology. Glenn Betteridge is a former lawyer who now works as a legal and health consultant. David McLay holds a PhD in biology and is a professional science writer.
This Research Snapshot is from their report, “HIV Non-disclosure and the criminal law: Establishing policy options for Ontario,” which was funded by the Ontario HIV Treatment Network and involved a research collaboration between York University, Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, HIV and AIDS Legal Clinic (Ontario), Black Coalition for AIDS Prevention, AIDS Committee of Toronto, and Toronto PWA Foundation.
Global: AIDS 2010 round-up part 2: Posters
This selection of posters presented in Vienna follows up from my previous AIDS 2010 posting on the sessions, meetings and media reporting that took place during last month’s XVIII International AIDS Conference. I’ll be a highlighting a few others in later blog posts, but for now here’s three posters that highlight how the law discriminates; why non-disclosure is problematic to criminalise; and how political advocacy can sometimes yield positive change.
In Who gets prosecuted? A review of HIV transmission and exposure cases in Austria, England, Sweden and Switzerland, (THPE1012) Robert James examines which people and which communicable diseases came to the attention of the criminal justice system in four European countries, and concludes: “Men were more likely than women to be prosecuted for HIV exposure or transmission under criminal laws in Sweden, Switzerland and the UK. The majority of cases in Austria involved the prosecution of female sex workers. Migrants from southern and west African countries were the first people prosecuted in Sweden and England but home nationals have now become the largest group prosecuted in both countries. Even in countries without HIV specific criminal laws, people with HIV have been prosecuted more often than people with more common contagious diseases.”Download the pdf here.
In Responsibilities, Significant Risks and Legal Repercussions: Interviews with gay men as complex knowledge-exchange sites for scientific and legal information about HIV (THPE1015), Daniel Grace and Josephine MacIntosh from Canada interviewed 55 gay men, some of whom were living with HIV, to explore issues related to the criminalisation of non-disclosure, notably responsibilities, significant risks and legal repercussions. Their findings highlight why gay men believe that disclosure is both important and highly problematic. Download the pdf here.
In Decriminalisation of HIV transmission in Switzerland (THPE1017), Luciano Ruggia and Kurt Pärli of the Swiss National AIDS Commission (EKAF) – the Swiss statement people – describe how they have been working behind the scenes to modify Article 231 of the Swiss Penal Code which allows for the prosecution by the police of anyone who allegedly spreads “intentionally or by neglect a dangerous transmissible human disease” without the need of a complainant. Disclosure of HIV-positive status and/or consent to unprotected sex does not preclude this being an offence, in effect criminalising all unprotected sex by people with HIV. Since 1989, there have been 39 prosecutions and 26 convictions under this law. A new Law on Epidemics removes Article 231, leaving only intentional transmission as a criminal offence, and will be deabted before the Swiss Parliament next year. Download the pdf here.
Global: AIDS 2010 round-up part 1: sessions, meetings and media reports
A remarkable amount of advocacy and information sharing took place during the XVIII International AIDS Conference held in Vienna last month. Over the next few blog posts, I’ll be highlighting as much as I can starting with a round-up of sessions, meetings, and media reports from the conference. A separate blog post will highlight posters, a movie screening and some inspirational personal meetings.
Sunday: Criminalisation of HIV Exposure and Transmission: Global Extent, Impact and The Way Forward
A meeting that I co-organised (representing NAM) along with the Global Network of People Living with HIV (GNP+) and the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network received quite a lot of coverage.
Criminalisation of HIV Exposure and Transmission: Global Extent, Impact and The Way Forward was a great success with many of the 80+ attendees telling me it was Vienna highlight. The entire meeting, lasting around 2 1/2 hours, has been split into eight videos: an introduction; six presentations; and an audience and panel discussion. The entire meeting can also be viewed at the NAM and Legal Network websites, with GNP+ soon to follow.
Reports from the meeting focusing on different parts of the meeting were filed by NAM and NAPWA (Aus) and I was interviewed by Mark S King for his video blog for thebody.com.
Richard Elliott of the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, Moono Nyambe from GNP+ and UNAIDS’ Susan Timberlake – all of whom took part in the meeting – were interviewed for a piece in Canada’s Globe and Mail, with the headline, U.S., Canada lead world in prosecuting those who transmit AIDS virus: Criminal charges are justified only when infection is intentional, activists contend.
The same day, an editorial in the Globe and Mail completely undermined the rather balanced article by stating, quite bluntly
Disclosing one’s status is, of course, a difficult and emotional journey, fraught with potentially negative consequences. HIV-positive people can be marginalized, and discriminated against in terms of housing, employment and social relationships. However, the collective rights of this minority group cannot take precedence over their individual responsibility not to infect others.
It concluded
But in Canada the law is clear: Exposure without disclosure is a crime. And that is a good thing.
Judging by the comments left by readers of both articles, although there is some sympathy for the person with HIV, there’s a long way to go before Canadian hearts and minds are won over by the anti-criminalisation advocacy movement.
Wednesday: Policing Sex and Sexuality: The Role of Law in HIV
Lucy Stackpool-Moore (IPPF) and Mandeep Dhaliwal (UNDP)co-chaired a satellite session on the Wednesday that included presentations by Anand Grover, UN Special Rapporteur on Right to Health, and my colleague Robert James of Birkbeck College, University of London.
Thursday: HIV and Criminal Law: Prevention or Punishment?
This debate included discussion of criminalisation from the point of view of increased stigma. Lucy Stackpool-Moore again contributed. The session was not only recorded by the rapporteur, Skhumbuzo Maphumulo, but also reported on by PLUS News.
Thursday: Leaders against Criminalization of Sex Work, Sodomy, Drug Use or Possession, and HIV Transmission
I’ve already included a blog posting on my presentation, which you can see here. The other presentations included Criminalization of HIV transmission and exposure and obligatory testing in 8 Latin American countries, presented by Tamil Rainanne Kendall. (Audio and slides here); Tanzania case study on how AIDS law criminalizes stigma and discrimination but also stigmatizes by criminalizing deliberate HIV infection, presented by Millicent Obaso (Audio and slides here); and If there is no risk and no harm there should be no crime. Legal, evidential and procedural approaches to reducing unwarranted prosecutions of people with HIV for exposure and transmission, presented by Robert James (and co-authored by yours truly). (Audio and slides here).
The session was also reported on by aidsmap.com.
Thursday: Late Breakers (Track F)
This session included three oral abstracts on criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission.
A quantitative study of the impact of a US state criminal HIV disclosure law on state residents living with HIV, presented by Carol Galletly. (Audio and slides here).
Roger Pebody of aidsmap.com provides an excellent summary of her findings here
Under [Michigan] state legislation, people with HIV are legally obliged to disclose their HIV status before any kind of sexual contact. Disclosure is meant to occur before sexual intercourse “or any other intrusion, however slight, of any part of a person’s body or of any object into the genital or anal openings of another person’s body”. This would include even fingering or the use of a sex toy.
Carol Galletly reported on a study with 384 people with HIV who live in Michigan (but recruitment methods and demographics were not fully described). Three quarters of respondents were aware of the law.
She wanted to see if the existence of the law had any impact on her respondents’ behaviour. Comparing those who were aware of the law with those who were not, people who knew about the law were no more likely to disclose their HIV status to sexual partners. Moreover they were not less likely to have risky sex.
On the other hand, approximately half of participants believed that the law made it more likely that people with HIV would disclose to sex partners. Having this belief was associated with being a person who did disclose HIV status to partners.
In fact a majority of participants supported the law. Individuals who Gallety characterised as possibly being marginalised were more likely to support the law: women, non-whites, people with less education and people with a lower income.
The two other presentations were: HIV non-disclosure and the criminal law: effects of Canada’s ‘significant risk’ test on people living with HIV/AIDS and health and social service providers, presented by Eric Mykhalovskiy (Audio and slides here) and Advocating prevention over punishment: the risks of HIV criminalization in Burkina Faso presented by Patrice Sanon (Audio and slides here).
Other media reports
Other reports mentioning the criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission published during the conference include:
A piece in the Montreal Gazette, headlined, Advocates raise concerns over prosecuting HIV-positive people
The troubling increase in the number of new HIV cases in Canada may be attributed to the country’s reputation of being a world leader in prosecuting HIV-positive people who fail to disclose their status, according to one group of AIDS advocates. “We’re looking at rising numbers of infection, especially among certain risk groups,” said Ron Rosenes, vice chair of Canadian Treatment Action Council. “And now we’re looking at the criminalization issue as one of the reasons people have been afraid to learn their status.”
Global: ‘Where HIV is a crime, not just a virus’ – updated Top 20 table and video presentation now online
Where HIV Is a Crime, Not Just a Virus from HIV Action on Vimeo.
Here is my presentation providing a global overview of laws and prosecutions at the XVIII International AIDS Conference, Vienna, on 22 July 2010.
Abstract: Where HIV is a crime, not just a virus: a global ranking of prosecutions for HIV non-disclosure, exposure and transmission.
Issues: The global (mis)use of the criminal law to control and punish the behaviour of PLHIV was highlighted at AIDS 2008, where Justice Edwin Cameron called for “a campaign against criminalisation”. However advocacy on this vitally important issue is in its infancy, hampered by lack of information on a local, national and international level.
Description: A global overview of prosecutions to December 2009, based on data from GNP+ Global Criminalisation Scan (http://criminalisation.gnpplus.net); media reports collated on criminalhivtransmission.blogspot.com and WHO Europe pilot human rights audit. Top 20 ranking is based on the ratio of rate per year/per HIV population.
Lessons learned: Prosecutions for non-intentional HIV exposure and transmission continue unabated. More than 60 countries have prosecuted HIV exposure or transmission and/or have HIV-specific laws that allow for prosecutions. At least eight countries enacted new HIV-specific laws in 2008/9; new laws are proposed in 15 countries or jurisdictions; 23 countries actively prosecuted PLHIV in 2008/9.
Next steps: PLHIV networks and civil society, in partnership with public sector, donor, multilateral and UN agencies, must invest in understanding the drivers and impact of criminalisation, and work pragmatically with criminal justice system/lawmakers to reduce its harm.
Video produced by www.georgetownmedia.de
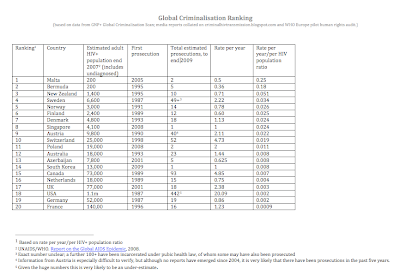 |
| This table reflects amended data for Sweden provided by Andreas Berglöf of HIV Sweden after the conference, relegating Sweden from 3rd to 4th. Its laws, including the forced disclosure of HIV-positive status, remain some of the most draconian in the world. Click here to download pdf. |
Global: Four anti-criminalisation advocacy resources launched at AIDS 2010
The XVIII International AIDS Conference held last week in Vienna was a hotbed of anti-criminalisation advocacy, including an extremely well-attended and well-received pre-conference meeting – Criminalisation of HIV Exposure and Transmission: Global Extent, Impact and The Way Forward – that I co-organised on behalf of NAM, along with GNP+ and the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network. We’re working on editing the video of the six presentations and panel discussions right now, and this should be ready later this week.
I’m also working on an article for NAM’s HIV Treatment Update that will synthesise all of the data and advocacy presented at the conference, and over the next week or so will be adding blog posts that highlight some of the work that I couldn’t include in the piece, as well as media reports focusing on criminalisation at the conference.
In the meantime, I’d like to draw your attention to four major advocacy resources that were launched at the conference.
HIV and the criminal law is a new online resource that I wrote and edited for the UK HIV information charity, NAM, and launched at AIDS 2010 in Vienna. A book version will be available in September 2010. Pre-order your copy here.
Preface by The Hon. Michael Kirby AC CMG and Edwin Cameron, Justice of the Constitutional Court of South Africa.
Introduction How this resource addresses the criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission.
Fundamentals An overview of the global HIV pandemic, and the role of human rights and the law in the international response to HIV.
Laws A history of the criminalisation of HIV exposure and transmission, and a brief explanation of the kinds of laws used to do this.
Harm Considers the actual and perceived impact of HIV on wellbeing, how these inform legislation and the legal construction of HIV-related harm.
Responsibility Looks at two areas of responsiblity for HIV prevention: responsibility for HIV-related sexual risk-taking and responsibility to disclose a known HIV-positive status to a sexual partner.
Risk An examination of prosecuted behaviours, using scientific evidence to determine actual risk, and how this evidence has been applied in jurisdictions worldwide.
Proof Foreseeability, intent, causality and consent are key elements in establishing criminal culpability. The challenges and practice in proving these in HIV exposure and transmission cases.
Impact An assessment of the impact of criminalisation and HIV – on individuals, communities, countries and the course of the global HIV epidemic.
Details: international resource and individual country data A summary of laws, prosecutions and responses to criminalisation of HIV exposure or transmission internationally, and key sources of more information.
The 2010 Global Criminalisation Scan Report (GNP+)
The 2010 Global Criminalisation Scan Report from the Global Network of People Living with HIV (GNP+) gives a global overview of the extent to which criminal and other laws have been used to prosecute people living with HIV for HIV transmission and exposure.
The full impact of these laws on the human rights of people living with HIV and on access to treatment, care and support has yet to be fully understood. However, the evidence presented here shows that there is no correlation between the HIV prevalence in a country and the willingness of countries to use criminal laws and other punitive measures to regulate transmission.
The report gives examples of instances where people living with HIV have expressed concerns about negative consequences that come from the overly broad use of laws in cases of transmission and exposure to HIV. This report highlights the urgent need for government reform and calls for the guided application of expert evidence and legal opinion to stem the swell of prosecutions and to counter the false premise of the perceived benefit of HIV-specific criminal laws.
Download a pdf of the Report here.
Responding to the Criminalization of HIV Transmission or Exposure: Resources for lawyers and advocates (Prepared by: Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, AIDES, Groupe sida Genève, GNP+)
In response to the increasing use of criminal law internationally, as well as to the great need to develop tools for lawyers representing people living with HIV, this kit provides both informative documentation to support lawyers in the preparation of their cases and selected publications that can ultimately be presented in court.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Detailed table of contents
- Publication information
- Section 1: Living with HIV
- Section 2: HIV transmission: the science
- Section 3: HIV/AIDS in a legal context: the use of criminal law in cases of HIV transmission or exposure
- Section 4: International recommendations on the criminalization of HIV
transmission and exposure- Section 5: Key court decisions internationally
- Section 6: Criminal law and HIV transmission and exposure at the national level
- Section 7: Additional resources
To view the entire resource visit the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network website. (Aussi disponible en français)
HIV Non-Disclosure and the Criminal Law: Establishing Policy Options for Ontario (Eric Mykhalovskiy, Glenn Betteridge and David McLay).
This report contributes to the development of an evidence-informed approach to using the criminal law to address the risk of the sexual transmission of HIV in the province of Ontario.
In recent years, the application of criminal law powers to circumstances of HIV exposure in sexual relations has emerged as a key HIV-related policy issue. In Ontario, people living with HIV/AIDS (PHAs), AIDS Service Organizations (ASOs), human rights advocates and others have raised concerns about the expansive use of the criminal law in addressing HIV-related sexual offences. They have raised questions about fairness in the application of the criminal law and about its negative consequences for PHAs and established public health and community-based HIV prevention strategies.
This report is rooted in these concerns. It responds to them in two ways. First, it explores various forms of evidence relevant to a thorough policy consideration of the use of the criminal law in circumstances of sexual exposure to HIV. Second, it proposes policy options for addressing the problems posed by the criminalization of HIV non-disclosure in Ontario.
This report emphasizes that uncertainty in the criminal law formulation of the obligation to disclose HIV+ status is foundational to current problems in the use of the criminal law to regulate the risk of the sexual transmission of HIV in Ontario.
It further emphasizes policy issues and problems arising at the nexus of science and criminal justice, in particular, those posed by the inconsistent use of complex scientific research by courts in deciding cases of alleged HIV non-disclosure.
Finally, the report underscores that the criminalization of HIV non-disclosure hinders established HIV prevention efforts and contributes to HIV-related stigma.
Download a pdf of the report here.
How could she go on living as if weren’t there [Trailer] (Sweden, 2010)
It is 1986. Lillemor is 19 And goes to France. She falls in love there; a love which results in her becoming HIV infected. Lillemor represses the fact that she has a lethal infection. She gets married and has children. She cannot bring herself to tell her husband that she is HIV positive. One day he finds out. Tabloid press and tv channels refer to her as the “HIV woman”. Lillemor’s husband divorces her, she loses custody of their children, and she loses her freedom.
Lillemor has now served a 30-month prison sentence for attempted grievous bodily harm. She was convicted for having had unprotected sex with her husband and for having gone through pregnancy and given birth to two children without first informing medical staff of the fact that she was HIV positive. Neither her ex-husband nor their children, now 7 and 8 years old, have contracted HIV.
This full length (73 minute) feature documentary is a stunning, heartbreaking exposition of how the stigma of HIV leads to Lillemor’s functional denial and ultimately her criminalisation, prosecution, conviction and incarceration.
PRODUCER/DIRECTOR INGELA LEKFALK
CINEMATOGRAPHY ANDERS BOHMAN STEFAN LARSSON
EDITING KERSTI GRUNDITZ
MUSIC LOUISE HOFFSTEIN
LARS PAULIN LASSE ENGLUND PETER KVINT
CHRISTOFFER DEMBY RESEARCH JENNY SJUNNESSON
More information: http://lekfalkab.se/eng/film_hurkundehon.html and at IMDB









