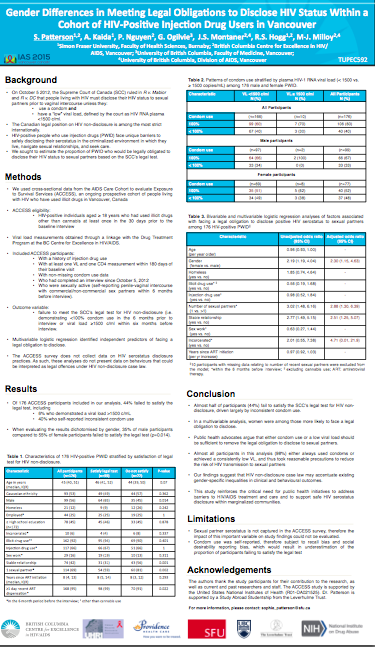
A new study presented to the International AIDS Society conference in Vancouver, Canada last week (IAS 2015) found that 44 per cent of participants within a research cohort of people who use injection drugs living with HIV in Vancouver would be legally obligated to disclose their HIV status to their sexual partners. Within the study, 65 per cent of male participants compared with only 45 percent of female participants satisfied the Supreme Court of Canada’s legal test for HIV non-disclosure, based on the October 2012 ruling in R v. Mabior.
Under current case law, people living with HIV must disclose their HIV status to a partner before sexual activity unless both a condom is used and a low HIV viral load is present.
The vast majority (98 per cent) of cohort participants in this study either self-reported always using a condom or achieved a low HIV viral load (<1500 copies/ml), and as such took steps to reduce the risk of HIV transmission to sexual partners. A person living with HIV who is appropriately treated and sustained on effective antiretroviral therapy will have an undetectable viral load, meaning the chance they will spread the virus is extremely low.
“The law as it currently stands places an additional veil of threat over an already vulnerable and criminalized population within one of Canada’s most impoverished communities,” said British Columbia Centre for Excellence in HIV/AIDS Director, and IAS 2015 conference co-chair, Dr. Julio Montaner. “Current non-HIV non-disclosure laws in Canada are not aligned with the state of the scientific evidence, and as a result create further stigma and fear around HIV.”
“The criminalization of HIV non-disclosure can affect people living with HIV in Canada in many ways,” said Valerie Nicholson, an Aboriginal woman living with HIV and the Chair of the Board of Directors at Positive Living BC. “People may face criminal charges for not disclosing, which can lead to lengthy and damaging criminal prosecutions – based on no scientific evidence. In the wider community, the law increases stigma and discrimination, does not account for power or control imbalances in relationships, compromises our ability to lead healthy sex lives and may introduce questions about the limits of confidentiality in the health care setting.”
The poster presentation of the study, “Gender differences in meeting legal obligations to disclose HIV status within a cohort of HIV-positive illicit drug users in Vancouver” is below.