English translation (para la versión en español, ver más abajo)
International organisations support the constitutional challenge against the law criminalizing HIV transmission in Veracruz
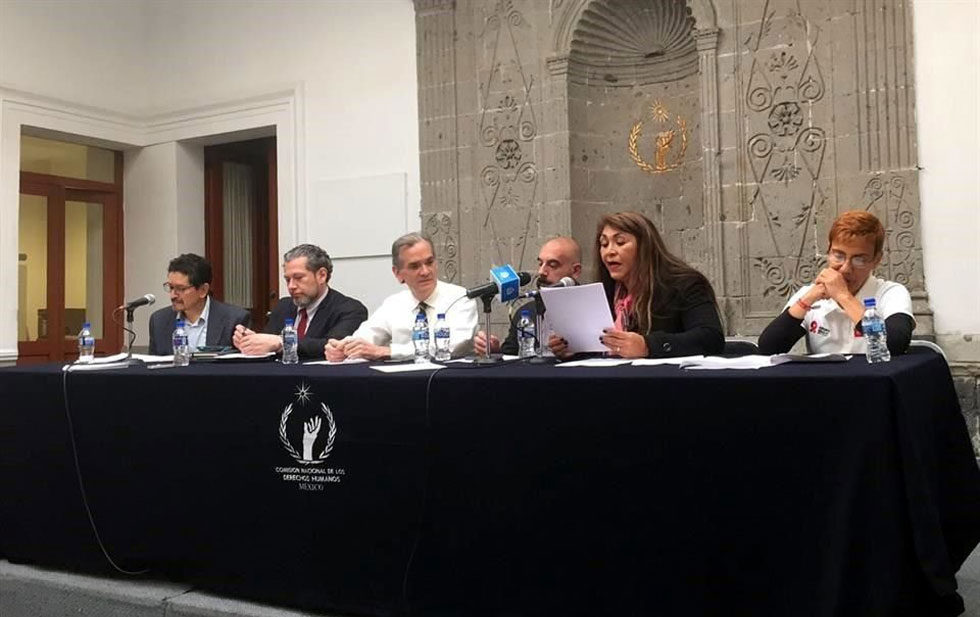
Before the amendment to Article 158 of the Criminal Code of Veracruz, entitled “Contagion”, which added the term Sexually Transmitted Diseases to the article, and was adopted on August 4, 2015 by the Congress of the State, the National Commission on Human Rights, in response to the request of the Multisectoral Group on HIV / AIDS and STIs of the State of Veracruz and other organisations of civil society, brought the constitutional challenge 139/2015 against the amendment to the Supreme Court of Justice of the Nation this past December.
This is because the legal reform indicates that among these infections, HIV and human papilloma virus are outlined and a penalty ranging from 6 months to 5 years in prison and a fine of up to 50 days salary is established for those “deceitfully” infecting another person of any sexually transmitted disease.
The reform presented by Deputy Monica Robles Barajas from the Ecologist Green Party of Mexico, was intended to “try to prevent the transmission of these infections, mainly to women and girls who are in a vulnerable position…”.
Unconstitutionality
For the CNDH, the new content of Article 158 of the Criminal Code of the State of Veracruz “generates a discriminatory treatment to the detriment of the people, and that criminalising the willful endangerment of disease transmission, generates two assumptions: that it concerns sexually transmitted infections and that it concerns serious diseases. “
In addition, he said the agency does not meet its objective of preventing the spread of sexually transmitted infections against women and girls, finding themselves in vulnerable situations, but that it create a differentiation based on the condition of certain types of infections, in this case of sexual transmission, and that it casts them as serious, a fact that is not real, because not all infections of this type are serious.
International support
A little after half a year after the appeal, organisations of international civil society such a HIV Justice Worlwide have delivered a letter to the Supreme Court of Justice of the Nation for the legal challenge to be considered as “there is no evidence that criminalising perceived or potential exposure to HIV or STI benefits prevention; however, there are serious concerns that criminalisation can cause considerable damage. “
The document submitted to the Court, reminds us that various international bodies such as UNAIDS, the Special Rapporteur on the right to health to the United Nations, the Global Commission on HIV and the Law and the World Health Organization, have recommended to governments to limit the use of criminal law to the extremely exceptional cases of intentional transmission of HIV (for example, when the person knows their own HIV positive status, acts with the intention to transmit HIV, and in fact transmit it).
The letter also notes that laws criminalizing HIV affect the rights of people with HIV because they cause confusion and fear about their duties under the law; they generate failures in the justice system, often as a result of inadequately informed and competent legal representation; they risk triggering prosecutions as a means of abuse or retaliation against a current or former partner; Police investigations are disproportionate and insensitive and can cause stigma and discrimination, and they promote sentences and disproportionate penalties.
In addition, fear of prosecution may discourage people, especially those belonging to those populations highly vulnerable to HIV, to get tested and know their status, because many laws apply only to those who are aware of their HIV status and thus prevent access to care and treatment because medical records can be used in evidence against them in the courts.
Worrying situation
Patricia Ponce, researcher at the Center for Research and Studies on Social Anthropology and member of the Multisectoral Group on STI and HIV / AIDS of the State of Veracruz, stated that the situation in the state is worrying because it is the region with the third highest number of cumulative cases of AIDS throughout Mexico, the second in HIV cases, the second in the number of women living with the virus and the second in the number of children affected by HIV.
Meanwhile, Edwin J. Bernard, global coordinator of the HIV Justice Network Worldwide, said that the fight against the epidemic requires the eradication of stigma and discrimination, not to add further through the legal system.
For the specific case of Veracruz, he explained that “if you want to protect women and girls from HIV, what should be done is to strengthen and empower women”.
Sean Strub, CEO of the Sero Project of the United States, explained that the existence of laws that criminalize HIV transmission is a public health issue because sanction reduces the possibility of new diagnoses.
“The best way to combat the criminalization of HIV is that people with the virus raise their hands to eradicate the situation,” he added.
Alejandro Brito, director of the civil organization Letra S, warned that if this situation is allowed to pass, “this can become a domino effect and similar changes could be approved in other states.”
In this regard, Ricardo Hernandez Forcada, director of the Programme for HIV AIDS and Human Rights at CNDH said that practically in every state, and even in federal criminal codes, there is a penalty for the transmission of sexually transmitted infections, and it is known that in Baja California Sur people have been jailed under that criterion.
——————————————————————————————————-
Organizaciones internacionales respaldan acción de inconstitucionalidad contra la ley que criminaliza transmisión del VIH en Veracruz
Ante la modificación al artículo 158 del Código Penal de Veracruz, denominado “Del Contagio”, a fin de adicionar el término Infecciones de Transmisión Sexual, aprobada el 4 de agosto de 2015 por el congreso de la entidad, la Comisión Nacional de Derechos Humanos, en respuesta a la petición del Grupo Multisectorial en VIH/sida e ITS del estado de Veracruz y otras organizaciones de la sociedad civil, interpuso la acción de inconstitucionalidad 139/ 2015 en contra de la reforma en la Suprema Corte de Justicia de la Nación en diciembre pasado.
Eso, debido a que la reforma legal señala que entre dichas infecciones se contempla al VIH y al virus del papiloma humano y se establece una pena que va de los 6 meses a los 5 años de prisión y multa de hasta 50 días de salario para quien “dolosamente” infecte a otra persona de alguna enfermedad de transmisión sexual.
La reforma, presentada por la diputada Mónica Robles Barajas del Partido Verde Ecologista de México, tenía la finalidad de “tratar de prevenir la transmisión de dichas infecciones, principalmente a las mujeres y las niñas que se encuentren en condición de vulnerabilidad…”.
Acción de inconstitucionalidad
Para la CNDH, el nuevo contenido del artículo 158 del Código Penal del Estado de Veracruz “genera un trato discriminatorio en perjuicio de las personas, ya que al tipificar como delito la puesta dolosa en peligro de contagio de enfermedades, genera dos supuestos: que se trate de infecciones de transmisión sexual y que se trate de enfermedades graves”.
Además, señaló el organismo, no cumple su objetivo de prevenir la transmisión de infecciones sexuales hacia mujeres y niñas, por encontrarse en condiciones de vulnerabilidad, sino que provocó una diferenciación basada en el padecimiento de cierto tipo de infecciones, en este caso de transmisión sexual, y calificarlas como graves, hecho que no es real, pues no todas las infecciones de este corte son graves.
Respaldo internacional
A poco más de medio año de haberse presentado el recurso, organizaciones de la sociedad civil internacionales como Red Justicia por VIH en todo el Mundo entregaron una carta a la Suprema Corte de Justicia de la Nación para solicitar la admisión del recurso legal tomando en cuenta que “no hay evidencia de que criminalizar la exposición potencial o percibida al VIH o ITS beneficie la prevención; sin embargo, hay serias preocupaciones de que la criminalización puede causar un daño considerable”.
En el documento entregado a la Corte, se recuerda que diversos organismos internacionales como el Programa Conjunto de las Naciones Unidas sobre el VIH/Sida, el Relator Especial del derecho a la salud de las Naciones Unidas, la Comisión Global de VIH y la Ley y la Organización Mundial de la Salud han recomendado a los gobiernos limitar el uso del derecho penal a situaciones extremadamente excepcionales casos de transmisión intencional de VIH (por ejemplo, cuando la persona conoce su propio estatus seropositivo, actúa con la intención de transmitir el VIH, y de hecho lo transmite).
La misiva también señala que las leyes que criminalizan al VIH afectan los derechos de las personas con VIH porque provocan confusión y miedo sobre obligaciones en virtud de la ley; generan fallas en los sistemas de justicia, a menudo como resultado de una representación legal inadecuadamente informada y competente; surgen amenazas que desencadenan el enjuiciamiento como medio de abuso o represalia contra una pareja actual o anterior; las investigaciones policiales son desproporcionadas e insensibles, pudiendo provocar estigma y discriminación, y propicia condenas y sanciones desproporcionadas.
Además, el miedo al procesamiento judicial puede desalentar a las personas, especialmente a aquellas pertenecientes a poblaciones altamente vulnerables al VIH, de examinarse y conocer su estatus, porque muchas leyes se aplican sólo a quienes son conscientes de su estatus seropositivo e impide el acceso a la atención y tratamiento porque las historias clínicas pueden ser usadas como evidencia en su contra en las Cortes.
Situación preocupante
Para Patricia Ponce, investigadora del Centro de Investigaciones y Estudios sobre Antropología Social Unidad Golfo e integrante del Grupo Multisectorial en ITS y VIH/sida del Estado de Veracruz, la situación en el estado es preocupante debido a que es la entidad con el tercer número más alto de casos acumulados de sida de toda la República Mexicana, el segundo de casos de VIH, el segundo en número de mujeres viviendo con el virus y el segundo con niños afectados por VIH.
Por su parte, Edwin J. Bernard, coordinador global de la Red Justicia por VIH en todo el Mundo, consideró que el combate contra la epidemia requiere erradicar el estigma y la discriminación, no añadirle aún más a través del orden jurídico.
Para el caso concreto de Veracruz, explicó que “si se quiere proteger a las mujeres y niñas del VIH, lo que se debe hacer es fortalecerlas y empoderarlas”.
Sean Strub, director ejecutivo de Sero Project de los Estados Unidos, explicó que la existencia de leyes que penalizan la transmisión del VIH son un asunto de salud pública porque sancionar reduce la posibilidad de realizar nuevos diagnósticos.
“La mejor manera de combatir la criminalización del VIH es que las personas con el virus alcen la mano para erradicar la situación”, añadió.
Alejandro Brito, director de la organización civil Letra S, advirtió que si se deja pasar la situación, “esta se puede convertir en un efecto domino y podrían aprobarse modificaciones similares en otros estados”.
Al respecto, Ricardo Hernández Forcada, director del Programa de VIH SIDA y Derechos Humanos de la CNDH, señaló que, prácticamente, en todos los códigos penales estatales, e incluso el federal, hay alguna penalización por la transmisión de infecciones de transmisión sexual, y se tiene conocimiento de que en Baja California Sur se ha encarcelado gente bajo dicho criterio.
Fuente: Notiese