
A new report published today (July 22nd 2022) by the HIV Justice Network (HJN) on behalf of HIV JUSTICE WORLDWIDE shows that the global movement to end HIV criminalisation continues to achieve remarkable successes, despite the many challenges that COVID-19 has brought.
Advancing HIV Justice 4: Understanding Commonalities, Seizing Opportunities provides a progress report of achievements and challenges in global advocacy against HIV criminalisation. The report generally covers a three year period ending 31 December 2021 where Advancing HIV Justice 3 ended. However, significant law reform developments that took place in the first quarter of 2022 are also included in report’s maps and analysis.
The successes
During the reporting period, four HIV criminalisation laws were repealed; another HIV criminalisation law was found to be unconstitutional; and six laws were ‘modernised’ (i.e. applied up-to-date science on HIV-related risk or harm and/or legal and human rights principles to limit the application of the law) five of which were in the United States.

In addition, we saw precedent-setting cases in four countries and policy recommendations or improvements in four further countries — all of which have the potential to limit the overly broad application of the law to people living with HIV based on HIV-positive status.
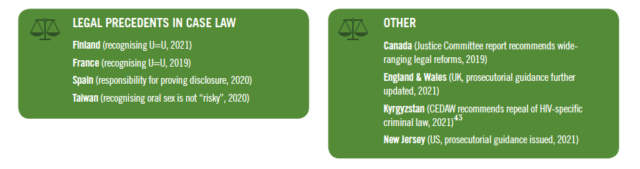
While legislative processes slowed down or stalled in some places due to COVID-19 diminishing capacity for advocacy, more HIV criminalisation laws were modernised or repealed in the United States than during any other time period, the realisation of a maturing PLHIV-led HIV decriminalisation movement that began a decade or more ago.
These outcomes were primarily due to sustained advocacy – most of it led by PLHIV networks working with allies – using a wide range of strategies. These are analysed in the report by HJN’s senior policy analyst, Alison Symington.
The challenges
However, too many HIV criminalisation cases and continued high numbers of HIV-related criminal laws continue to be of great concern, requiring more attention, co-ordinated advocacy, and funding.
Our global audit of HIV-related laws found that a total of 82 countries (111 jurisdictions) have criminal laws that are HIV-specific. Of those, we are aware of 52 jurisdictions in 35 countries that have applied their HIV-specific criminal laws.
Another 89 jurisdictions in 48 countries have applied non-HIV-specific, general criminal laws in an overly broad manner since the first prosecution in 1986.
Our case analysis shows that HIV criminalisation continues to disproportionately impact women, racial and ethnic minorities, migrants, gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people, and sex workers.
Although the total number of cases has diminished in some US states as well as in countries that were previously HIV criminalisation hotspots – Canada, Czech Republic, Norway, Sweden, and Zimbabwe – too many unjust prosecutions and convictions continue to be reported.
During the reporting period, we recorded 275 cases in HJN’s Global HIV Criminalisation Database. However, when we include case numbers from several Eastern European and Central Asian countries that provide official data, we estimate almost 700 criminal cases over the reporting period.
Notwithstanding the limitations of tabulating cases globally, the highest number of reported cases during the period covered by this report were in:

The report is available to download in English, French, Russian and Spanish.
- Download the report (PDF, 51 pages, 4.9MB)
- Téléchargez le rapport (PDF, 55 pages, 6MB)
- Скачать отчет (PDF, 61 страницы, 7MB)
- Descargue el informe (PDF, 58 páginas, 6.9MB)
Acknowlegements
Advancing HIV Justice 4 was conceived and edited by HJN’s executive director, Edwin J Bernard, and HJN’s senior policy analyst, Alison Symington. Alison Symington researched and wrote all chapters except for ‘Global Overview’, which was researched and written by Edwin J Bernard, using data collected by Sylvie Beaumont and analysed by Tenesha Myrie.
Additional input was provided by: Gonzalo Aburto (The Sero Project), India Annamanthadoo (HIV Legal Network), Stephen Barris (Ex Aequo), Sophie Brion (International Community of Women Living with HIV), Janet Butler-McPhee (HIV Legal Network), Nyasha Chingore-Munazvo (AIDS and Rights Alliance for Southern Africa), Kenechukwu Esom (United Nations Development Programme), Elie Georges Ballan (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS – UNAIDS), Alfredo González (Hondureños Contra el SIDA), Julian Hows (HIV Justice Network), Deidre Johnson (Ending Criminalization of HIV and Overincarceration in Virginia Coalition), Cécile Kazatchkine (HIV Legal Network), Svitlana Moroz (Eurasian Women’s Network on AIDS), Immaculate Owomugisha Bazare (Uganda Network on Law Ethics and HIV/AIDS), Stephen Page (Nevada HIV Modernization Coalition), Cedric Pulliam (Ending Criminalization of HIV and Overincarceration in Virginia Coalition), Florence Riako Anam (Global Network of People Living with HIV), Mianko Ramaroson (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS – UNAIDS), Demario Richardson (Missouri HIV Justice Coalition), Sean Strub (The Sero Project), and Alexandra Volgina (Global Network of People Living with HIV).
We would especially like to acknowledge the courage and commitment of the growing number of people living with HIV and allies around the world who are challenging laws, policies and practices that inappropriately regulate and punish people living with HIV. Without them, this report — and the victories reported herein — would not have been possible.
We gratefully acknowledge the financial contribution of the Robert Carr Fund to this report.